
The Traffic Accident Reconstruction Origin -Article-


The Traffic Accident Reconstruction Origin -Article-
|

|
Appendix B
The FOIL Method
|
Definitions |
|
|
Monomial |
An algebraic expression which is either a constant or a product of constants and variables. * |
|
Polynomial |
The sum of one or more monomials. * |
|
Binomial |
A polynomial which contains two monomials. |
|
Trinomial |
A polynomial which contains three monomials. |
|
Term |
An algebraic expression all of whose parts are connected by multiplication (and/or division). * |
We square a binomial by multiplying it by itself. An easy way to remember how to do this is the FOIL method. The acronym, FOIL, means First Outer Inner Last.
In this example, we have ![]() .
.
We can write this as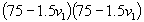 .
.
Multiply the First terms that appear in each binomial (75 and 75); we get 5625.
Next, multiply the Outer terms in each binomial (75 and
![]() ); we get
); we get
![]() .
.
Now, multiply the Inner terms in each binomial (![]() and
75); we get
and
75); we get
![]() .
.
Finally, multiply the Last terms in each binomial ![]() ; we get
; we get
![]() .
.
Now we add the like-terms of the resulting polynomial ![]()
The like terms are ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
This yields ![]() .
.
Now we add all the terms together (and arrange the terms in standard order) to get our final
trinomial, (![]() ).
).
|
The FOIL Method |
|
|
Copyright 1998 by Andrew S. Rich. All rights reserved.
*
Goodman, Arthur, and Hirsch, Lewis. Understanding Elementary Algebra. Third ed. St. Paul: West Pub. Co., 1994
|
Copyright ©
|